Week in Regulation
June 6, 2016
Another $4.7 Billion in Regulation
The unrelenting pace of regulation continued this week as regulators published another $4.7 billion in costs. Annualized burdens were $2 billion, compared to $1.2 billion in environmental and energy savings benefits. Thanks to a Department of Education proposal, paperwork declined by 6,800 hours. Final fracking standards and proposals to tighten water heating efficiency and the renewable fuels standard for 2017 and 2018 led the week. The per capita regulatory burden for 2016 is $332.
Regulatory Toplines
- New Proposed Rules: 36
- New Final Rules: 61
- 2016 Total Pages of Regulation: 36,136
- 2016 Final Rules: $86.4 Billion
- 2016 Proposed Rules: $20.9 Billion
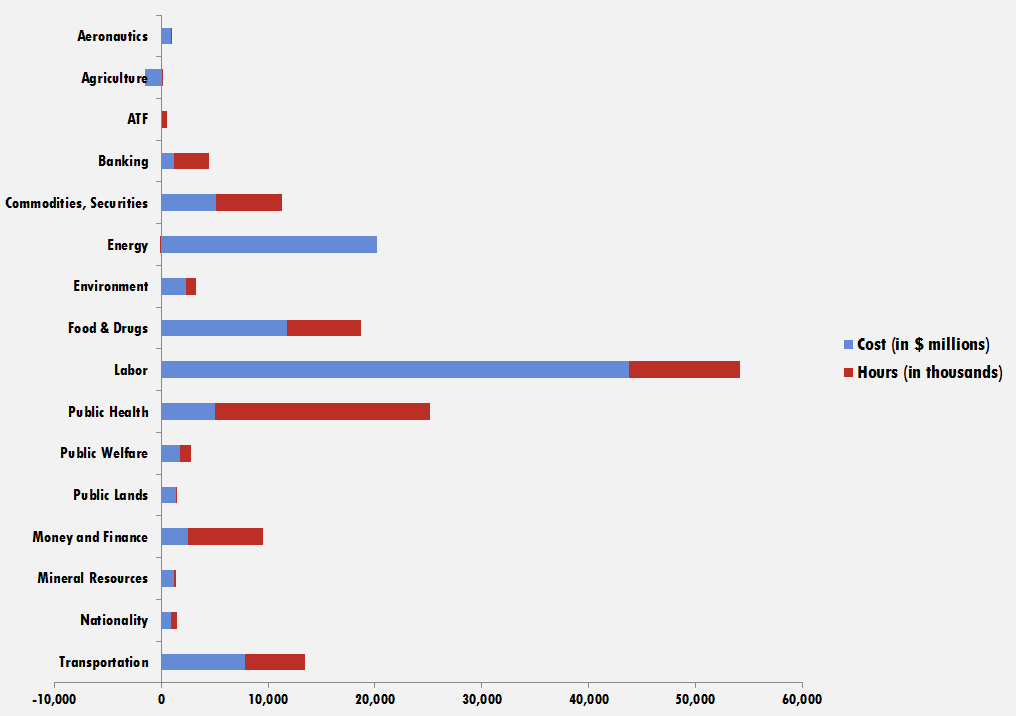
The American Action Forum (AAF) has catalogued regulations according to their codification in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). The CFR is organized into 50 titles, with each title corresponding to an industry or part of government. This snapshot will help to determine which sectors of the economy receive the highest number of regulatory actions.
The leader in net present value costs was a proposal from the Department of Energy (DOE) to increase commercial water heating equipment efficiency. During the life of the rule, it will cost $2.5 billion; annualized costs are $144 million, against $571 million in benefits. There are currently four additional efficiency standards waiting approval at the White House.
The administration also finalized another round of fracking standards in a bid to limit methane emissions. EPA and the Department of Interior have already issued fracking rules, but this measure was aimed specifically at oil and gas extraction and the release of greenhouse gases and volatile organic compounds that contribute to pollution. The measure will impose roughly $500 million in annual costs, but net annual benefits are expected to be $170 million.
EPA also proposed its renewable fuels standard for 2017 and 2018. In its benefit-cost analysis, the agency provided three illustrative costs of the rule: one for soybeans ($453 million to $683 million), one for Brazilian sugarcane ethanol ($290 million to $585 million), and for corn ethanol ($245 million to $288 million). According to the agency, these total illustrative costs range from $535 million to $971 million. EPA did not monetize the benefits, but estimates that it would reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Affordable Care Act
Since passage, based on total lifetime costs of the regulations, the Affordable Care Act has imposed costs of $48.5 billion in final state and private-sector burdens and 171.4 million annual paperwork hours.
Dodd-Frank
Click here to view the total estimated revised costs from Dodd-Frank; since passage, the legislation has produced more than 73.9 million final paperwork burden hours and imposed $36.2 billion in direct compliance costs.
Total Burdens
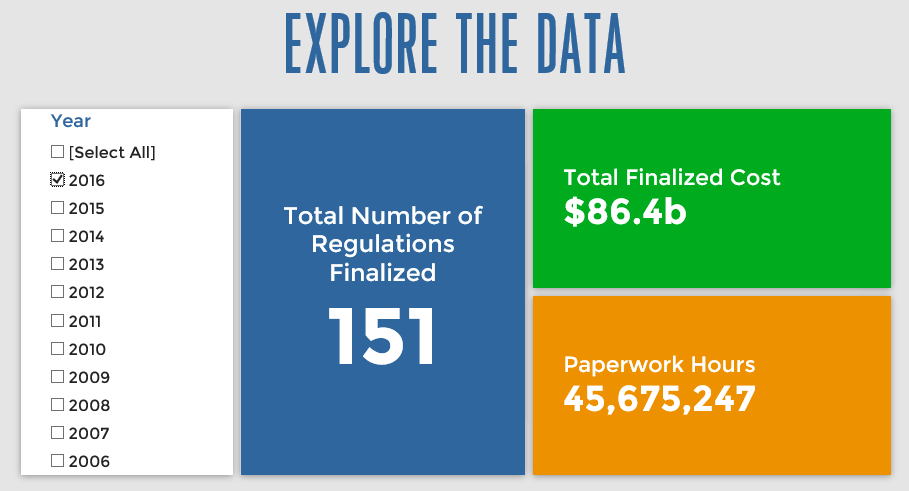
Since January 1, the federal government has published $107.3 billion in compliance costs ($86.4 billion in final rules) and has imposed 64.5 million in net paperwork burden hours (45.6 million from final rules). Click below for the latest Reg Rodeo findings.