Insight
March 10, 2022
President Biden’s Executive Order on Crypto Regulation and Digital Assets
Executive Summary
- President Biden has signed an executive order instructing a wide range of agencies to consider the regulatory consequences of cryptocurrencies and other digital assets, giving the agencies six months to provide detailed current state assessments including policy recommendations.
- The executive order represents only very early-stage development of a unified federal approach to crypto regulation; nevertheless, this work presages a whole-of-government approach to digital asset regulation that until now has lacked clear federal oversight, left market participants without protections, and lacked the support and backing of the U.S. government.
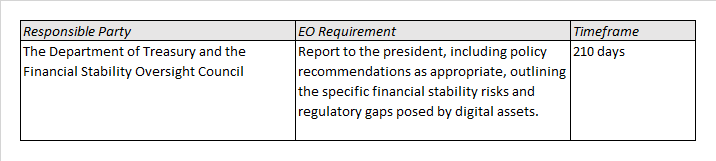
- A significant portion of the executive order is devoted to the development of a U.S. central bank digital currency, or digital dollar, demonstrating a surprising degree of interest by the administration and directing agencies to consider implications with a view to potential implementation.
Context
On March 9, 2022 President Biden signed a long-awaited executive order (EO) embarking on a whole-of-government, comprehensive approach to the regulation of cryptocurrencies and other digital assets. The EO calls for the financial regulatory agencies to study digital assets across six key priorities:
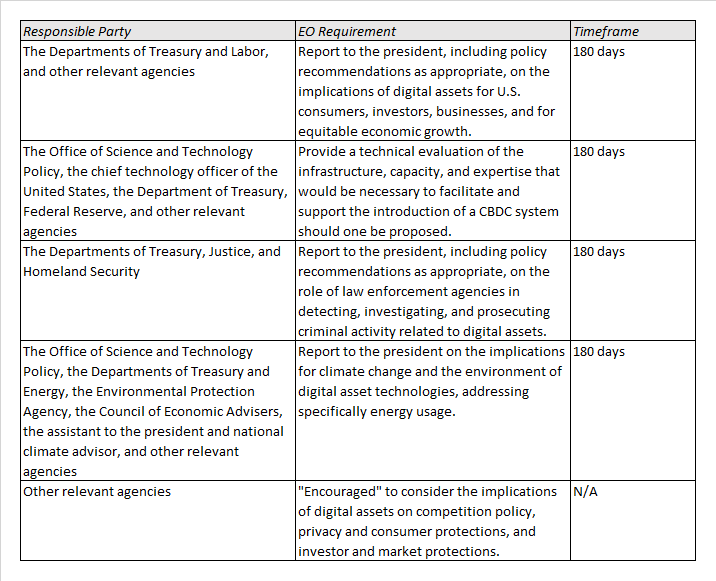
- consumer and investor protection, with a view particularly to the financial risks posed by inadequate protection of digital assets and cybersecurity;
- financial stability, as certain digital asset players and platforms scale in size and complexity without concomitant regulatory oversight;
- illicit finance, with crypto playing a role in money laundering, cybercrime and ransomware, narcotics and human trafficking, the financing of terrorism, and even allowing countries to avoid sanctions regimes;
- U.S. leadership in the global financial system and economic competitiveness, noting that American leadership in the global financial system must be “reinforce[d]”;
- financial inclusion, as crypto provides unique opportunities to reduce costs in the traditional banking sector and service the under- or unbanked; and
- responsible innovation, given that certain tech developments have wide-ranging implications touching sectors from finance and security to the environment.
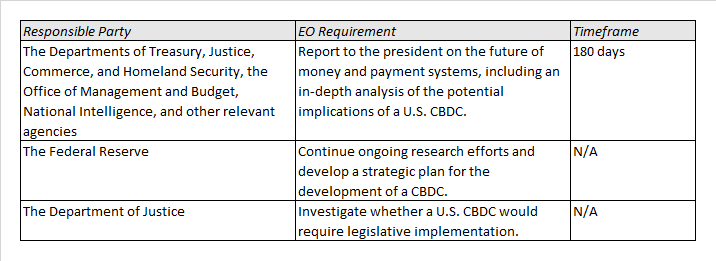
The EO places particular focus on the Biden Administration’s policy on the development of a U.S central bank digital currency (CBDC), noting that 100 other countries are currently exploring or piloting their own CBDC. Central bank money is reflected in currency issued and held by the Federal Reserve (the Fed). Digital currency represents both money held in digital form (for example, in a bank account) and new classes of digital assets including cryptocurrencies. A CBDC represents the combination of both – digital currency issued and backed by a central bank.
The Contents of The Executive Order
Policy and Actions Related to U. S. Central Bank Digital Currencies
The Biden Administration places “the highest urgency on research and development efforts into the potential design and deployment options of a United States CBDC,” and directs agencies to consider “the actions required to launch a United States CBDC if doing so is deemed to be in the national interest.” The order also notes the specific risks and benefits flowing from internationally interoperable CBDCs.
Measures to Protect Consumers, Investors, and Businesses
Digital assets and digital asset trading platforms pose new and increased risks of crimes, including fraud and theft, with the potential for disparate financial risk to vulnerable market populations. Even where digital assets are not abused, data asset actors may require protection that don’t currently exist in law.
Actions to Promote Financial Stability, Mitigate Systemic Risk, and Strengthen Market Integrity
While it is difficult to argue that the crypto and digital asset markets presently have systemic implications, digital assets reached a combined market capitalization of $3 trillion in November 2021, up from approximately $14 billion in early November 2016. The market possesses significant potential for scale and must address if not current then future financial stability risks posed by digital assets.
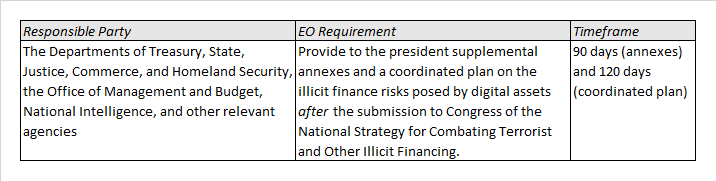
Actions to Limit Illicit Finance and Associated National Security Risks
Digital assets and cryptocurrencies are attractive as both target and facilitator for a wide range of cybercrimes including money laundering, terrorist and proliferation financing, fraud and theft schemes, and corruption.
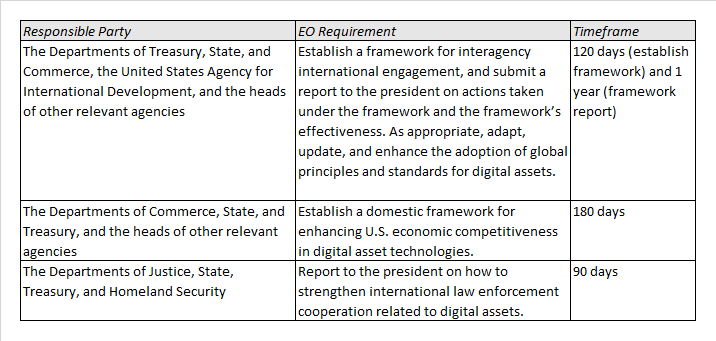
Policy and Actions Related to Fostering International Cooperation and United States Competitiveness
Technological developments are increasingly cross-border and benefit from international cooperation. The United States remains committed to existing work performed in conjunction with critical international partners, including through fora such as the G7, G20, FATF, and FSB.
Conclusions
For a market that has fluctuated between $1-$3 trillion over the course of the Biden presidency, the president’s EO on crypto and digital assets represents a formative moment – crypto regulation has until now faced a patchwork of at times inconsistent agency directives which has left consumers in need of regulatory protection. By creating a predictable regulatory environment, the U.S. government can spur growth in the development of digital assets and assist American fintechs to compete in global markets, with the potential that eventually this competition will occur via a U.S. digital dollar. Perhaps the most beneficial result will simply be the conferral of a kind of formal legitimacy, with the market capitalization of cryptocurrencies increasing 6.2 percent in the 24 hours following the release of the executive order. With effort from the various financial services regulatory agencies, the crypto Wild West can be tamed.