Insight
January 13, 2022
The Potential Impacts of the Build Back Better Act’s Drug Policies
Executive Summary
There is a perception that the drug pricing proposals in the House-passed Build Back Better Act (BBBA) are more modest and less threatening to medical innovation than those of the draconian H.R. 3 proposal. Policymakers, the media, and the public should understand that this is a deeply flawed impression. This insight summarizes the BBBA’s key drug policy provisions and examines their potential impacts. It finds that the BBBA’s drug policies would dramatically curtail future innovation and imperil the economic benefits the United States derives from the biopharmaceutical sector.
Key Points:
- The BBBA would establish an explicit government price-setting regime for pharmaceuticals, reaching into all corners of the U.S. health sector, both public and private.
- The BBBA does not establish a true “negotiation” of drug prices in Medicare; rather it would empower the secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) to dictate prices to manufacturers who would have little to no leverage.
- The BBBA would enshrine a unique and punitive 95 percent excise tax on gross profits of a therapy if the manufacturer does not agree to the secretary’s demands.
- The BBBA would establish a ceiling price, but unlike past proposals there is no floor price below which the secretary would be unable to force further concessions.
- Under the BBBA, for the first time, the federal government would cap the price of all drugs throughout the entire health care system by prohibiting any drug’s price from increasing faster than the rate of inflation.
- The BBBA proposals would harm consumers through reduced innovation and higher launch prices for drugs and therapies.
- One recent study found that the BBBA would result in 135 fewer new drug approvals, 188 fewer new indications for existing therapies, and a reduction of 331.5 million life years among patients.
- The combination of price setting by the HHS secretary and inflation penalties would likely reduce generic and biosimilar market entry, putting at risk potential savings and improved treatment options for millions of Americans.
- Price controls will essentially eliminate future improvements in insulins.
- BBBA’s inflation penalties are likely to result in higher launch prices and could drive price increases commensurate with inflation for therapies whose prices would not increase under current law.
- The BBBA would harm and endanger the expansive economic activity generated by the biopharmaceutical industry in the United States.
- The BBBA would reduce biopharmaceutical industry revenue by $2.9 trillion through 2039 and puts at risk a U.S. biopharmaceutical sector that generates more than $1 trillion in economic activity annually, employs more than 800,000 workers, and supports more than 4 million jobs across the U.S. economy.
- In the mid-1980s, as European countries imposed stringent price controls, Europe saw a flight of investment in drug development and manufacturing to the United States. Under the BBBA, the United States would risk a similar loss in competitiveness to countries such as India and China that are aggressively seeking to bolster their own biopharmaceutical sectors.
- There are better ways to lower drug prices than the BBBA.
- Congress should discard the remainder of the BBBA and focus on pursuing bipartisan reforms to Medicare Part D, similar to the redesign included in the BBBA.
- Legislative changes to drug rebates, like those pursued through rulemaking under the Trump Administration, would ensure that patients with high drug costs receive meaningful assistance.
- The single best way to bring down prices is to increase supply and competition; policymakers should remove regulatory barriers to new therapies and follow-on products coming to market, while also working to ensure enforcement of laws targeting anticompetitive practices.
Introduction
Annual health care spending in the United States increased 9.7 percent in 2020, totaling $4.1 trillion. While the COVID-19 pandemic has played a role in recent increases, health care spending and costs have both been growing rapidly for years. In 2020, 19.7 percent of the U.S. economy was devoted to health care spending.[1] Given these trends, policymakers across the political spectrum have long been concerned with constraining health care cost growth. But while conservatives have sought to address this policy challenge by promoting choice and competition in the private market, progressives have focused on reducing profits for health care companies and increasing the federal government’s role in providing and paying for care. Most notably, progressive politicians and activists have long been eager to target the profits of pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Prescription drugs, however, make up a relatively small percentage of total health care spending. According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), retail prescription drug spending made up just 8.4 percent of all U.S. health care spending in 2020.[2] While those figures do not account for therapies administered by providers in hospitals, nursing homes, or similar settings, the consulting firm Altarum estimates that non-retail prescription drug spending accounts for 4.5 percent of overall health care expenditures annually.[3] Though total spending on prescription therapies is not a large share of overall health spending, patients are more likely to bear the cost of medication directly due to the high coinsurance and deductibles increasingly common to drug coverage. Concern over the increasing cost of many biopharmaceutical therapies is therefore bipartisan, but progressives have consistently pursued policies that would constrain future innovation and restrict American patients’ access to the broadest range of therapies.
Much ink has been spilled over the obvious flaws of the Elijah E. Cummings Lower Drug Costs Now Act (H.R. 3), Speaker Pelosi’s legislation aimed at constraining prescription drug prices, but far less attention has been given to the drug policies that were included in the House-passed Build Back Better Act (BBBA).[4] In fact, there is a widespread perception that, because H.R. 3 was not included verbatim in the BBBA, the BBBA’s drug price provisions are less egregious and pose far less risk to consumers and the U.S. biopharmaceutical sector. This understanding is inaccurate.
This paper summarizes the BBBA’s key drug policy provisions and examines their potential impacts. It finds that the BBBA’s drug policies would dramatically curtail future innovation and would imperil the economic benefits the United States derives from the biopharmaceutical sector.
Key Drug Pricing Policies in the BBBA[5]
While action on the BBBA has stalled in the Senate, the House-passed version of the legislation contains a number of drug-related policies, in particular, Medicare negotiation of drug prices, inflation penalties, new regulation of insulin products and prices, and reforms to the Medicare Part D prescription drug benefit.
Medicare Negotiation for Drug Prices
Under the BBBA, beginning in 2025, the secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) would be authorized to “negotiate” the prices of up to 10 “negotiation-eligible drugs.” In 2026 and 2027, the cap increases to 15 drugs annually, and rises to 20 drugs in 2028 and beyond. Part B drugs—those drugs administered by a medical provider in a hospital, nursing home, or similar setting—would be exempt until 2027. Additionally, all insulin products would automatically be available for negotiation beyond the yearly caps.
A negotiation-eligible drug is defined as a small-molecule or biologic (including authorized generics) treatment that has had Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for at least seven years for a small-molecule drug or 11 years for a biologic that is among the 50 single-source drugs with the highest total expenditures in Part B or Part D. Orphan drugs or “low-spend” drugs are excluded, with low-spend being defined as a drug or biologic on which Medicare spends less than $200 million annually (adjusted by the consumer price index in future years). The reduced prices would be effective after an additional two years, meaning small-molecule drugs would have prices reduced nine years after approval and 13 years for biologics.
The BBBA would set a ceiling for negotiated price of between 40-75 percent of the non-federal average manufacturer price (AMP)—the average price paid by wholesalers, net of prompt pay discounts—scaling down depending on how far the drug is past its initial exclusivity period. There would, however, be no floor below which HHS could not demand price concessions. Unlike H.R. 3, the negotiated price would not be directly applied to the private health care market, but the negotiated rate or “maximum fair price” would be publicized.
In order to provide the secretary with leverage in negotiations, the legislation would establish an excise tax specifically on sales of drugs the secretary has targeted for negotiation but for which the manufacturer has not agreed to the secretary’s target price. The excise tax would be applied for any period in which the manufacturer is in “non-compliance.” The tax would start out at 65 percent of sales of the therapy for the first 90 days of non-compliance, increasing at regular intervals until topping out at 95 percent for any period of non-compliance beyond 270 days.
Inflation Penalties
The BBBA would establish penalties for drugmakers if they increase the price of a particular therapy faster than the rate of inflation. For drugs covered by Part D, the AMP would be assumed as the base price of the drug for the purpose of tracking price increases. A drug’s AMP would be benchmarked to October 2020, while inflation would be benchmarked to September 2021. Drugmakers could still increase their prices above inflation, but they would have to write a check for the difference. For example, if a drug’s AMP was $110 per unit in October 2020, and the inflation-adjusted AMP in 2023 is $120, but the actual AMP is $130, the manufacturer would have to pay the government $10 for every unit sold in 2023. The Part D inflation cap would apply to all drugs with a price of more than $100 per patient, per year.
In Part B, the principle is largely the same with a few differences. The price of the drug to be considered would be the Average Sales Price (ASP). ASP would be benchmarked to July 2021, while inflation would be benchmarked to September 2021. While both penalties would take effect in 2023, the Part B penalty would be assessed quarterly, while the Part D penalty would be paid annually. The penalty would be applied to all single-source drugs in Part B with costs exceeding $100 per patient, per year—and biologics would still be considered single source even if there were biosimilar competitors. Biosimilars would also be subject to penalties if their price is above that of the reference product.
Insulin Price Restrictions
The House-passed BBBA specifically targets insulin prices, making all insulin products automatically subject to Medicare negotiation. The BBBA would also unilaterally limit cost-sharing for insulin through Part D to $35 per month.
The BBBA would intercede in the group and individual insurance markets to limit patient insulin costs. Starting in 2023, health insurers offering group or individual health insurance coverage would be required to provide coverage for at least one of each insulin dosage form (vial, pump, or inhaler) of each type of insulin (rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, and premixed). Further plans would be required to limit patient costs for insulin to no more than either $35 for a 30-day supply, or an amount equal to 25 percent of the negotiated price of the insulin product for a 30-day supply—net all price concessions—whichever is lower.
Medicare Part D Reforms
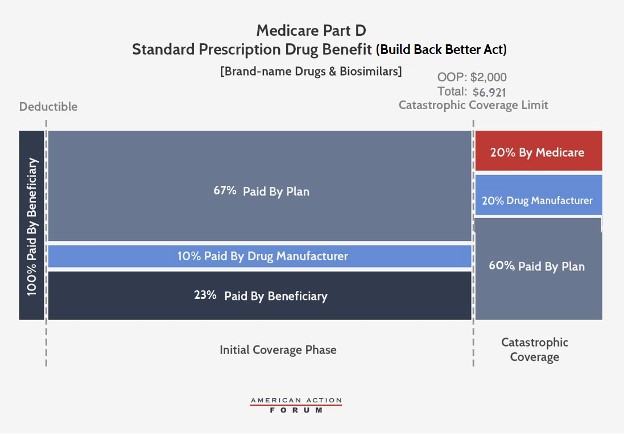
The House-passed BBBA undertakes a significant redesign of the Medicare Part D program, beginning in 2024, aimed at realigning plan and manufacturer incentives to constrain drug prices and to limit beneficiaries’ out-of-pocket (OOP) costs. The broad framework of the proposal—originally outlined by the American Action Forum’s (AAF) Tara O’Neill Hayes in 2018—has garnered bipartisan support, although there have been partisan differences over some of the details.
Under the BBBA, brand-name and biosimilar drug manufacturers would be liable for 10 percent of costs in the initial coverage phase and 20 percent in the catastrophic phase. Government reinsurance would fall to 20 percent for brand-name drugs and biosimilars and to 40 percent for generic drugs. Insurer liability in the catastrophic phase would increase to 60 percent for all drugs. The catastrophic phase would begin at $2,000 in OOP costs, capping beneficiary costs at that point.
The BBBA would also reduce beneficiaries’ coinsurance liability to 23 percent in the initial coverage phase (from 25 percent currently) and their premium liability to 23.5 percent (from 25.5 percent currently). Consequently, the federal premium subsidy rate would rise to 76.5 percent (from 74.5 percent) and insurer liability in the initial coverage phase would be 77 percent for generic drugs and 67 percent for brand-names and biosimilars.
Last, the BBBA would allow for beneficiaries’ OOP costs to be “smoothed” over the course of the year, rather than potentially having to pay as much as $2,000 in a single month.
While the BBBA version of the Part D redesign retains the 10 percent manufacturer share in the initial coverage phase that was added in the H.R. 3 version of the proposal, the legislation would lower the manufacturer share in the catastrophic phase from 30 percent in H.R. 3 to 20 percent, while AAF initially proposed 9 percent (note that AAF used 9 percent because that was determined to be the rate at which pharmaceutical companies would be responsible for the same level of costs at the time the original analysis was done, while AAF was neutral on whether manufacturers’ share of costs should increase).
Negative Impacts of the BBBA’s Drug Policies
The claim that that drug prices are higher than they reasonably should be is widely accepted. Progressive policymakers and activists in particular are quick to argue that drugmaker profits are higher than appropriate, or that manufacturers should only be able to pocket a “reasonable”—but undefined—profit. Part of the issue is that many do not acknowledge the high risk associated with pharmaceutical development. On average it takes more than a decade to bring a drug to market, and most therapies never get there. Between 2011 and 2020, only 7.9 percent of compounds that started Phase 1 clinical trials made it to market.[6] Calculating how much was spent on a particular drug’s development and then calculating a “fair” percentage markup for profit fails to account for investment in unsuccessful research efforts, or the inherent risk investors take when they provide research and development (R&D) capital to innovators. A reasonable return on investment (ROI) will look different if the risk of failure is higher, and investors expect a higher ROI in exchange for the risks related to pharmaceutical development relative to other investment options. In the absence of sufficient ROI, venture capital for pharmaceutical innovation will become increasingly scarce.
While the Part D redesign proposal in the BBBA does have a measure of bipartisan support, and aims to correct perverse incentives within the program, the overall impact of the combined policies would be to strangle innovation, limit access to new therapies for U.S. patients in the future, and endanger the economic benefits of a vibrant U.S.-based biopharmaceutical sector.
Overall Impact on Innovation
At the most basic level, any policies that reduce pharmaceutical industry revenue will have downward pressure on future innovation. In a recent paper from the University of Chicago, Tomas Philipson and Troy Durie estimate that a 1 percent reduction in pharmaceutical industry revenue leads on average to a 1.54 percent drop in R&D spending.[7] This does not mean that any policy that reduces industry revenue is inherently misguided, but policymakers need to be cognizant about the potential impacts of the policies they advance. Further, punitive policies aimed primarily at reducing drug company revenue—rather than those addressing specific market failures or perverse incentives enshrined in existing law—will have negative long-term impacts far outweighing any short-term satisfaction derived from “sticking it” to manufacturers.
AAF researchers have documented the potential impact on innovation of previous policies aimed at reducing pharmaceutical prices, specifically the Trump Administration’s International Price Index (IPI) proposal, and Speaker Pelosi’s H.R. 3. These proposals differ notably from the BBBA in that they tied price controls to the price of a drug in designated foreign countries. As such, these analyses cannot be directly applied to the BBBA, but they do provide some context for the potential impact of this legislation’s price controls.
According to analysis by AAF’s O’Neill Hayes in 2019, comments to CMS on the aborted IPI proposal, if that demo had been applied to all Part B drugs—expenditures for which equal roughly $30 billion—industry revenues would have been reduced approximately $9 billion per year. Considering that the cost of successfully bringing a drug to market has been estimated at approximately $2.87 billion, the $9 billion in lost revenue per year potentially attributable to the IPI proposal would be equivalent to the cost of three new medicines each year, or 30 fewer new therapies over 10 years. In the case of H.R. 3’s Average International Market (AIM) price, drug prices would be capped at 120 percent of the index, rather than 126 percent in the IPI proposal, and the capped price would be applied to all U.S. payers rather than limited to Medicare Part B, which accounts for only 10 percent of all drug expenditures in the United States. [8] If the effect on drug development of the AIM price were similar to the impact of the IPI, expanding those effects to 100 percent of the U.S. market would be the equivalent of 30 fewer drugs per year or 60 percent of the total number of new drugs approved by the FDA in 2021.[9] Extrapolated over 10 years, H.R. 3 would have potentially reduced industry revenue by the equivalent cost of 300 new therapies. Of course, these proposals would be unlikely to result in dollar-for-dollar reductions in R&D, so the actual number of lost therapies would be lower. These estimates are also not directly applicable to the BBBA because, whereas these past policies restrict drug prices to a limited range based on established international prices, the BBBA would implement a system of open-ended and steep price concessions based on domestic prices and enforced by a staggering 95 percent tax on gross profits of a particular therapy when a manufacturer fails to meet HHS’ price demands.
Philipson and Durie, in a robust analysis of the BBBA provisions published November 2021, estimate the legislation would reduce industry revenue by an astronomical $2.9 trillion through 2039. They attribute $1.77 trillion to the inflation rebates, $986.9 billion to government “negotiation,” and $138.1 billion to the Part D reforms. Using their estimates of the impact of revenue reductions on R&D spending, the authors calculate that the BBBA would result in 135 fewer new drug approvals by 2039, and that further disincentive to researching additional indications will lead to 188 fewer new indications for existing therapies over the same period. The authors also estimate that the policies would result in 331.5 million fewer life years through 2039. Significantly, the authors only apply the inflation limits to Medicare, but the inflation penalties will limit pricing in the private market as well, leading to even greater impacts on future innovation. They also assume that prices will be set at the absolute highest amount allowed under the BBBA, but there is no price floor, and the HHS secretary would have substantial leverage to force price concessions well below the maximum price.
Rather than being more limited in its impact on innovation than previous drug pricing proposals, the BBBA’s deleterious effects would be at least comparable to past proposals such as H.R. 3, and potentially even larger.
It should also be noted that the BBBA’s heavy intervention in the insulin market, popular though those provisions are likely to be, will almost certainly end substantive innovation around insulin products and delivery mechanisms, as there will be little financial incentive for companies to continue to invest in their development.
Medicare Negotiation: Dressed up Price-Fixing
Democrats in their political messaging have long touted the need to “let Medicare negotiate drug prices.” The idea that the federal government would make no effort to get the best deal possible on a service or good intuitively feels wrong—though it is unfortunately relatively common across federal programs—so much so that even former President Trump embraced the left’s rhetoric and called for Medicare to negotiate drug prices. This messaging, however, misstates the reality of how Medicare pays for drugs. One might think from these talking points that no negotiations occur between the Medicare prescription drug program and drug manufacturers. In fact, the Medicare Part D program has robust negotiation and competition built into its very fabric.[10] Insurance companies offering drug coverage through Part D negotiate directly with manufacturers to get the best price they can for the drugs they provide. Getting a lower price benefits the prescription drug plan directly and allows it to lower premiums to attract seniors. In this way, the negotiations drive down premiums, copays and overall drug costs. Plans are able to drive discounts by offering preferred placement on their formularies to specific therapies in exchange for lower prices. In some cases—with the exception of specific protected classes of drugs—a plan might decline to cover a particular therapy at all as part of its negotiations. This would be a problem if there were only one formulary for all beneficiaries, but beneficiaries are able to choose between a wide range of plan offerings, allowing them to select a plan that best fits their needs. In 2022, the average Medicare beneficiary will have a choice of 23 stand-alone Part D plans, and 31 Medicare Advantage plans that include drug coverage.[11]
To protect this competitive environment, federal law prohibits the HHS secretary from interfering in the negotiations between plans and manufacturers. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) has long held that simply removing this “noninterference” clause would not result in any savings for the program because the secretary has no beneficiaries to negotiate on behalf of, and no leverage for driving price concessions.[12] Giving the secretary the legal authority to negotiate directly with manufacturers will either result in a single negotiated price for each drug—which will then have to be accepted by all insurers—thus undermining the competitive structure of Part D, or it will result in nothing.
The authors of the BBBA have opted for the former, allowing the secretary to set prices that will be applied to all plans, and giving the secretary leverage to force price concessions via the draconian 95 percent excise tax on gross profits for any therapy whose manufacturer is unwilling to meet the secretary’s price demands. Setting aside the negative long-term effects of the strict price controls envisioned by the BBBA, proponents should dispense with the fiction that this would resemble anything remotely like a negotiation. Given the 95 percent excise tax—the like of which appears nowhere else in federal law—the secretary would be free to wield against noncompliant innovators, “price extortion” would be a more honest label for this provision than “price negotiation.”
Ramifications of Inflation Penalties
While the BBBA would not apply Medicare’s negotiated prices for drugs to non-federal programs, the most significant implication of the BBBA’s dollar-for-dollar penalties on price increases that exceed the rate of inflation is that, for the first time, the federal government would be unilaterally capping drug prices nationwide, both in federal programs and in the private market. This shift in the federal government’s posture toward private markets, negotiations, and competition cannot be overstated.
Additionally, the BBBA sets the inflation benchmark to a later date than the price benchmark. As a result, the legislation extracts additional revenue from drugmakers to pay for the BBBA’s other provisions—reinforcing the claim that at least part of the purposes of the drug provisions is simply to generate money to pay for unrelated new spending. If the policy benchmarked both drug price and inflation to September 2021, CBO would likely have assumed that drugmakers would keep their price increases to the rate of inflation. There would be savings due to slower price growth over time, but they wouldn’t be huge. By capturing the recent inflation spike and back-dating drug prices far enough to ensure that pricing decisions already made are subject to the new policy, Democrats ensured that the CBO score included additional revenue from penalties, and that manufacturers would have to pay for Democrats’ last year of inflationary spending policies.
Faced with restrictions on future pricing flexibility, drugmakers would be incentivized to increase initial launch prices in response to inflation penalties. While these products would eventually be subject to HHS’s price-setting regime, those forced price concessions would not take effect until years after the product’s launch, further incentivizing manufacturers to maximize initial profits through higher launch prices.
It is worth noting that the BBBA drug provisions would be introduced in an environment of general price inflation not seen in four decades. The imposition of price controls on insulin and other drugs would guarantee that they will be underpriced in real terms in very short order—a recipe for further inefficiency and damage to innovation incentives. At the same time, there would be drugs that will see their prices rise at inflation—because the BBBA essentially blesses such a price rise as “legitimate”—even though no such increase is merited on the fundamentals. The result would be prices that are too high in real terms and a harm to consumers.
Economic Damage to the Biopharmaceutical Sector
The biopharmaceutical sector in the United States creates more than $1 trillion in economic activity and employs more than 800,000 workers—at an average compensation over twice the national average. More broadly, the industry supports more than 4 million jobs across the U.S. economy, and generated over $67 billion in federal, state, and local tax revenue in 2017 alone.
The BBBA’s policies aimed at reducing industry revenues put this vibrant economic engine at risk. In 1986, R&D investments by pharmaceutical firms in Europe exceeded R&D in the United States by roughly 24 percent.[13] Following the imposition of government price controls in many European countries, and consequently the reduced return on investment, R&D spending by pharmaceutical companies grew at an annual rate of just 5.4 percent in the European Union, compared with 8.8 percent growth in the United States. As such, more than half of the world’s pharmaceutical R&D investments have been made in the United States since the turn of the century, whereas less than 30 percent has been invested in Europe.[14] While shifting patterns of investment are the product of many factors, historically R&D and manufacturing investments have moved away from countries in which strict price control regimes are implemented. With countries such as India and China, among others, aggressively seeking to bolster their own biopharmaceutical industries, the BBBA would put at risk the economic benefits the United States derives from the sector and would advantage other countries in their efforts to lure away investments currently being made in this country.
Impact on Generic and Biosimilar Market Entry
Another under-appreciated point of concern with the BBBA is the way the legislation’s provisions could disincentivize future development of generic and biosimilar therapies. Historically, flow-on products have led to significant cost savings for American patients and have been a primary driver of prescription medications’ relatively small share of total health care expenditures. Ironically, the more successful the HHS secretary is in leveraging the BBBA’s punitive excise tax to force price concessions, the fewer generic and biosimilar products are likely to come to market. Follow-on products are able to dramatically undercut name-brand drugs and biologics on price because they do not have the same R&D expenditures and because their lower prices allow them to achieve larger market shares. But if the price difference between a name-brand drug, subject to the secretary’s price controls, and a new generic is marginal or even non-existent, the ability of a generic to gain market share will be reduced.
It may be that HHS is able to drive sufficient price concessions—at the cost of future innovation—to offset some of the lost savings due to a decimated generic and biosimilar pipeline, but lower prices are not the only benefit of follow-on products. Different patients respond differently to the same medication, so a robust pipeline of follow-on therapies ensures patients are more likely to have access to a therapy without unwanted side effects. Reduced market entry of generics and biosimilars could lead to fewer options for doctors to help patients avoid adverse reactions and side effects.
Pharmaceutical Policy Options to Consider
While progressives spin their collective wheels trying to target drugmaker profits, there are some viable solutions for tackling drug prices in ways that promote competition and better align the incentives inherent in federal law.
Drug Rebates
In 2019 the Trump Administration proposed significant changes to the structure of drug rebates. While Congress has delayed and sought to repeal this rulemaking, it would be wise to reconsider. Under current law, drug manufacturers typically provide significant rebates for drugs provided at the pharmacy counter (averaging nearly 30 percent in Medicare Part D), especially for drugs with competing alternatives. These rebates are most commonly paid to pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) in exchange for preferred placement on the insurance plan’s drug formulary. The PBMs, however, do not usually share those rebates directly with patients, instead typically using the rebates to hold down premium costs for everyone. But using rebates on high-cost drugs to broadly lower premiums instead of passing them through to beneficiaries results in the (high-cost) sick subsidizing the (low-cost) healthy, which seems counter to the intent of an insurance product.
The rebate rule, if implemented, would change that practice. Drug rebates would no longer be allowed unless they are completely passed through to the patient at the point of sale. This change would almost certainly lead to increased premiums Part D premiums, which is why there has been opposition. Those increases are likely to be minimal, however, as the cost increase would be spread across all beneficiaries. On the other hand, the reduced cost-sharing expenses that the highest-cost beneficiaries would see should outweigh those premium cost increases, resulting in a net benefit to patients. Those patients with the highest costs would see the greatest benefit. The Trump Administration could only propose changes to affect rebates in the Medicare program through rulemaking; if Congress were to enact a legislative version of the rebate rule, however, it could extend the policy throughout the insurance system, which is an approach worth consideration.
Competition and Increased Supply
History has proven the best way to reduce the price of a good for which there is growing demand is to increase its supply through competition. For drug pricing, that means bringing generics and biosimilars to market to compete with brand-name drugs.
A now-classic example of this phenomenon is the Hepatitis C treatment, Sovaldi, which contributed over $3 billion to 2014 expenditures alone.[15] While the drug was quite expensive, it is important to note two things. First, Sovaldi—and its eventual competitors—provided a cure for what had been up until that point a costly-to-manage chronic disease. Second, as competitors joined the market, the price of Sovaldi was cut in half. Where there is competition, prices come down. The FDA has been doing its part by approving a record number of generic drugs and biosimilars.[16] But other barriers to unlocking robust market competition remain.
Legal Enforcement of Competition Policy
Often, once a generic drug has been on the market long enough, it acquires enough of the market share that the brand-name manufacturer stops producing its version of the drug. In many cases, the price reaches a low enough point at which other generic competitors also exit the market, leaving a sole manufacturer. In some high-profile cases we see what amounts to abuse of monopoly power—that sole manufacturer taking advantage of its position and dramatically increasing its price once there is no more competition and consumers have no choice but to purchase the now high-priced drug. In these cases, it should be treated as the abuse that it is and prosecuted where appropriate.
Prosecuting such monopoly abuses may require new authority for the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC’s mission is “to prevent business practices that are anticompetitive or deceptive or unfair to consumers.” The FTC notes that it has limited authority to take action against a company that has drastically raised the price of a drug, depending on the reason for the increase.
Medicare Part D Reform
On a positive note, the BBBA takes a step in the right direction on drug policy by realigning incentives in the Part D program—and Congress should work to enact reforms along these lines. While the structure of the BBBA’s Part D reform is largely the same as AAF’s original proposal—as well as House Republican’s proposal in H.R. 19 and the proposal included in H.R. 3—there are some differences. AAF considered capping beneficiary OOP costs between $2,500 and $4,000 annually. The BBBA caps OOP costs at $2,000, significantly below what beneficiaries are expected to pay before moving into the catastrophic phase under current law. One potential improvement, recognizing budgetary constraints and the need to balance savings for beneficiaries with costs for taxpayers, would be a slightly higher OOP. This could be coupled with a reduction in beneficiary coinsurance below the cap, which would benefit more enrollees—since most will never reach the OOP cap—while still providing substantial savings for taxpayers and enrollees who do reach the cap.
Conclusion
The BBBA’s drug pricing provisions have been bemoaned by progressives as far short of what is necessary, and touted by moderate Democrats as more reasonable and less draconian than past efforts such as H.R. 3. Both these views are fundamentally flawed. The BBBA would make large-scale changes to drug policy at the federal level and reach deep into private insurance and contracts. These policies would have widespread, negative impacts on the development of future therapies, new indications for existing therapies, and the economic benefits the United States derives from a vibrant biopharmaceutical sector. If the BBBA’s policies are enacted in totality, American patients will suffer, American leadership in medical research will be diminished, and a vibrant engine of economic development for American workers and investors will be strangled.
Notes
[1] https://www.healthaffairs.org/doi/10.1377/hlthaff.2021.01763
[2] https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/NationalHealthExpendData/NationalHealthAccountsHistorical
[3] https://altarum.org/sites/default/files/uploaded-publication-files/Altarum%20Projections%20of%20the%20Non-Retail%20Dru.pdf
[4] https://www.americanactionforum.org/testimony/testimony-on-the-lower-drug-costs-now-act-h-r-3/
[5] https://www.americanactionforum.org/research/key-health-policy-provisions-of-the-build-back-better-act/
[6] https://go.bio.org/rs/490-EHZ-999/images/ClinicalDevelopmentSuccessRates2011_2020.pdf?_ga=2.112327436.987275036.1641911607-1139759599.1641911607
[7] https://cpb-us-w2.wpmucdn.com/voices.uchicago.edu/dist/d/3128/files/2021/08/Issue-Brief-Drug-Pricing-in-HR-5376-11.30.pdf
[8] https://www.americanactionforum.org/comments-for-record/comments-to-cms-on-proposed-international-pricing-index-for-medicare-part-b-drugs/
[9] https://www.fda.gov/drugs/new-drugs-fda-cders-new-molecular-entities-and-new-therapeutic-biological-products/novel-drug-approvals-2021
[10] https://www.americanactionforum.org/research/competition-and-the-medicare-part-d-program/
[11] https://www.kff.org/medicare/issue-brief/medicare-part-d-a-first-look-at-medicare-prescription-drug-plans-in-2022/
[12] https://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/108th-congress-2003-2004/reports/fristletter.pdf
[13] https://www.nber.org/papers/w12676
[14] https://www.abpi.org.uk/facts-and-figures/science-and-innovation/worldwide-pharmaceutical-company-rd-expenditure-by-country/
[15] https://www.cms.gov/Research-Statistics-Data-and-Systems/Statistics-Trends-and-Reports/Information-on-Prescription-Drugs/index.html
[16] https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/FDAInBrief/ucm625627.htm